Common Types Of Foundation Materials
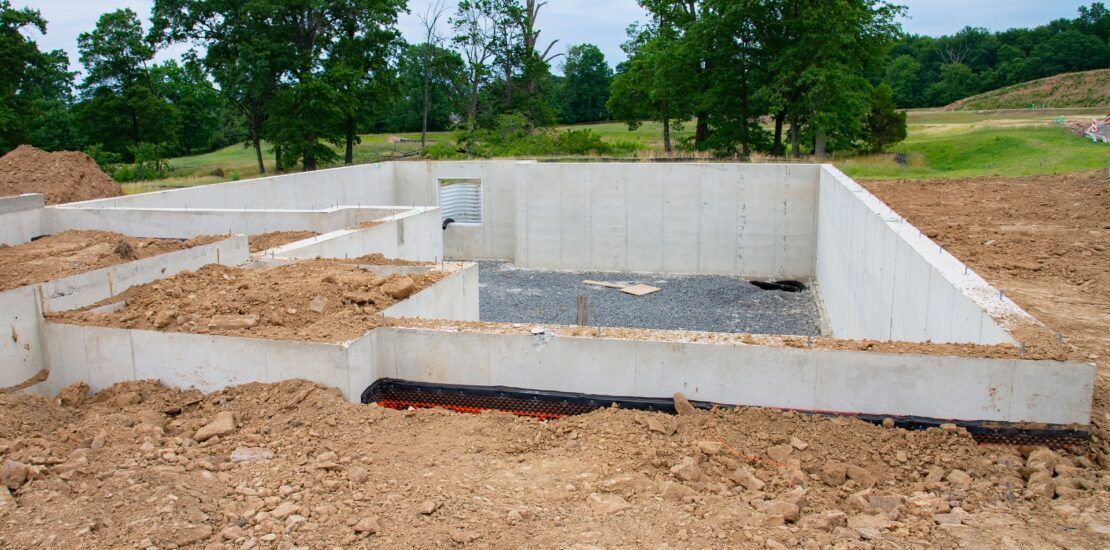

Without a solid foundation, every structure would quickly crumble and collapse. This is why the foundation materials used have to be as durable as possible.
Why is that?
Supporting the building is just one of the reasons why. Building foundations are often subject to the elements and thus need to withstand everything from moisture to pesky rodents. Thus, foundation materials have to resist water damage and the lateral forces of the saturated soil.
Today, we’ll discuss the best foundation materials while also learning more about foundations and their many types.
Let’s get started!
All about the foundation
Before describing the different types of foundation materials, we should take a closer look at the foundation itself.
In simple terms, the foundation is the lowest part of the structure, and its role is to support the weight from the upper portions of the building and transfer it to the ground below.
The foundation provides lateral stability for the whole structure, but it also provides a level surface for the construction of the lower level of the building. Additionally, it ensures the load distribution is even.
Lastly, the foundation prevents the soil movement effect and solves the problem of soil scouring.
There are several types of foundations used in construction, with the two most common being::
This type of foundation sits closer to the ground. They aren’t as deep, so the additional stability is achieved by making the foundation very wide. Shallow foundations take significantly less time to build, which makes them cost-effective.
As a result, they are used mostly for smaller structures.
There are several types of shallow foundations:
1. Individual footing
2. Combined footing
3. Strip footing
4. Raft or mat foundation
As the name suggests, deep foundations transfer the weight of the building into the earth. They are strong and can support heavier loads. Deep foundations are what make skyscrapers and other tall structures possible.
One popular type of deep foundation is a pile foundation. It consists of tubes filled with concrete connected with beams that support the building structurally. The heavy load is distributed between these tubes equally.
Foundation materials
A building is only as sturdy as the foundation materials. This is why the choice of materials matters.
Some of the most common materials include:
1. Wood
While wood isn’t one of the sturdiest materials, if treated properly, wood is one of the most formidable foundation materials. It’s also the most cost-effective option, especially when compared to concrete.
When pressure treated and coated with different chemicals, wood becomes sturdy and resistant to rotting. More importantly, the chemical treatment makes it resistant to pests such as rodents and termites.
2. Stone
Stone was one of the most common foundation materials pre-World War I. This is why you can usually spot them in historic districts and such.
Nevertheless, even today, stones are strong, durable, inexpensive materials that are a mainstay for low piers and curtain walls. When laid with mortar, stones do a good job keeping water at bay and keeping out vermin such as termites.
3. Concrete and concrete blocks
The king of materials used in foundation construction is concrete. It’s sturdy, strong in compression, and very durable. It’s also moisture resistant and watertight.
However, the most favorable property of concrete is that it can be cast into every shape possible, thus simplifying the foundation construction process. For instance, if you made a curtain wall out of concrete, you’d only require a narrow trench with very little formwork.
Since cement can be very pricy, concrete foundations are usually expensive.
A slightly cheaper way to go about this is to use concrete blocks. Concrete block foundations are simple to construct as there is no need for formwork, and since concrete blocks are large, it doesn’t take a lot of time to lay them up.
The downside of concrete blocks is that they are hard to waterproof. Walls made from this material simply don’t resist the elements as effectively as poured concrete does.
4. Aggregates
Aggregates are raw materials in making concrete. To be more precise, they make up between 60% and 80% of the entirety of a concrete mix. They provide the concrete with bulk and the strength necessary to resist heavy loads and elements.
The best quality concrete requires high-quality aggregates. They have to be clean, strong, and free of chemicals. This is because too many absorbed chemicals or too many impurities could cause negative effects on the final product.
Aggregates can consist of different materials, such as slag, sand, crushed stone, or gravel.
5. Fly ash
Fly ash is a gray powder that is a side-effect of burning powdered coal. Due to its pozzolanic properties (high reactivity with lime that leads to cementitious compounds), it is known as supplementary cementitious material.
Fly ash is a lot cheaper than a pure cement mix of concrete. As such, the mixes using fly ash are less costly and are usually referred to as performance mixes.
6. Sand
Sand is a filler material in concrete as it fills up the pores between aggregates. As such, it’s one of the main factors in concrete affecting both its texture and strength. Without sand, the final product would be weak and difficult to pour, which would eliminate it as one of the best foundation materials.
7. Brick
Brick foundations are popular for a good reason. Brick is durable, but more importantly, it’s the best option if temperature insulation is one of your biggest concerns. For example, basements in houses with brick foundations will be warm in the winter and cool in the summer.
There is a downside, however. While brick is cheaper than concrete, it also takes longer for these foundations to be built, and ultimately, they might end up costing more than a concrete foundation. Additionally, since bricks are stacked on top of each other to build the foundation, the brick foundation wall will take up more space inside the house.
8. Steel
Steel is treated to be rust-free and stainless and it’s most commonly used as a reinforcing material in foundation construction. It’s usually utilized in the form of rods arranged perpendicular or parallel to each other.
Steel is strong, durable, and resistant to natural disasters, making it one of the best and most cost-effective foundation materials around.
Strong materials for a strong foundation
Some people wrongfully assume that if the structure of the building is strong, the materials used in the foundation don’t matter. However, that’s patently false.
While the main role of the foundation is to support the building, it can also affect so many other factors. The foundation materials play a key part in the longevity of the building itself. Different materials have different strengths and weaknesses. Such as heat insulation characteristics and moisture resistance.
The foundation materials might make all the difference if your house stays in tip-top shape if you live in an area with high humidity, for example.
The next time you go looking for a house, don’t forget to check the foundation because it can give you a better idea of how easy future maintenance might be.
Disclaimer: The information on this website and blog is for general informational purposes only and is not professional advice. We make no guarantees of accuracy or completeness. We disclaim all liability for errors, omissions, or reliance on this content. Always consult a qualified professional for specific guidance.
Recent Posts
6742 Forest Hill Blvd #336, West Palm Beach, FL 33413 US
Mon-Fr: 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
Eastern Standard Time
Disclaimer: The information provided on this website is for general purposes only. It should not be construed as legal/financial advice or the formation of a consultant/client relationship. Prior results do not guarantee similar outcomes.
All Rights Reserved.
Website Designed & Managed by Oamii.